The blood in your veins acts as an essential transportation system for oxygen and nutrients that need to be distributed throughout your body. Oxygen and nutrients are traded with waste that needs to be filtered out of your body. When you have damaged blood vessels, your blood circulation doesn’t function as effectively, commonly referred to as poor circulation.
What is Poor Circulation?
Poor circulation mainly occurs in the arms or legs when blood flow is reduced, preventing cells in the body from receiving adequate oxygen.
Think of your circulatory system as a delivery network, constantly transporting blood, oxygen, and nutrients to every corner of your body. When everything is running smoothly, your heart, veins, arteries, capillaries, and other blood vessels work together to keep this delivery system efficient. Blood brings in the essentials to your cells and clears away waste, much like a well-organized courier service.
However, when there’s damage or interference in your blood vessels—whether due to blockages, narrowing arteries, or faulty valves—this delivery system runs into roadblocks. Blood flow becomes sluggish, especially when trying to reach areas farthest from your heart, like your fingers and toes. It’s as if your delivery driver keeps hitting detours, causing delays and making it difficult for supplies to reach their destination.
Poor circulation occurs when blood flow is significantly reduced due to interference in a part of your body. Obstacles in your blood vessels can make it harder for your blood to travel through to the parts of your body farthest from your heart. When your blood has difficulty circulating, the cells in your body get less oxygen which makes it harder for them to function properly.
The biggest concern with poor circulation is that your cells aren’t getting the oxygen and nutrients they need to stay healthy. Without a steady supply, your cells struggle to do their jobs and remove waste efficiently. Over time, this can lead to a series of symptoms and complications, especially in your legs and feet.
Symptoms of Poor Leg Circulation
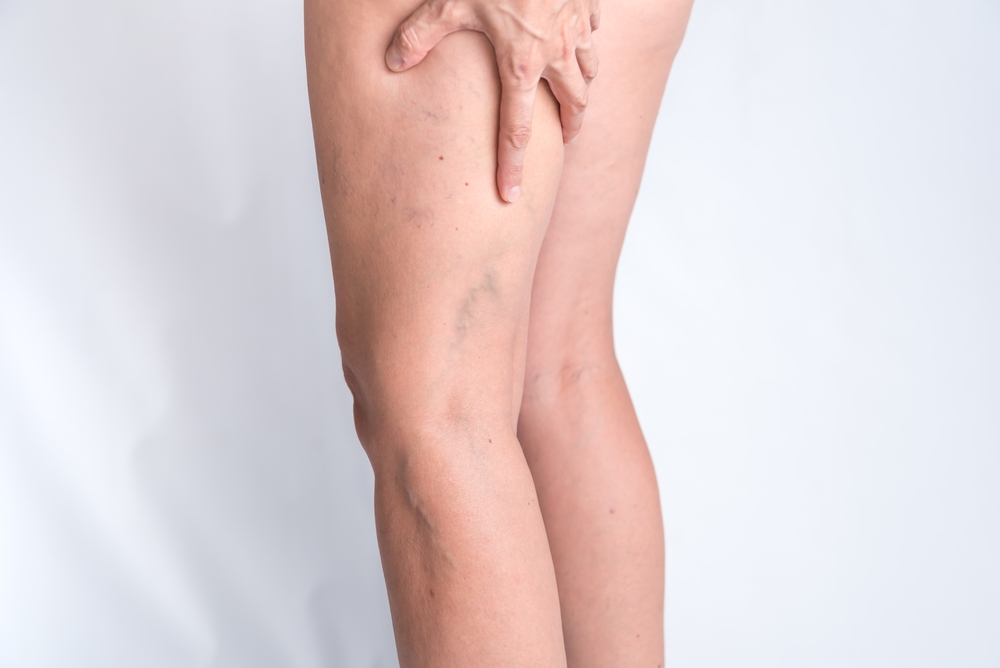
If you over 40 years old, overweight, diabetic, or struggle to get active, here are key symptoms to keep an eye out for:
- Bulging Veins: Often enlarged, bulging veins are can appear twisted and bulge due to blood pooling and pressure on vein from lack of circulation.
- Cold feet or toes: Cold feet or toes can signal poor circulation, and can sometimes be a symptom of more serious vascular conditions like peripheral artery disease or PAD.
- Numbness: Numbness can also signal lack or proper circulation to the legs, and can be a result of PAD and/or diabetes.
- Pale or blue skin color: Reduction of blood flow to the lower extremities can cause pale or blue appearance to skin.
- Sore or weak muscles when walking: Poor circulation in the legs can make the legs muscles feel week or sore, with relief when only at rest – this is a key sign of improper blood flow to the legs.
- “Pins and needles” sensation: Usually described as a “tingling” in the legs, this type of sensation is commonly linked to poor circulation in the legs.
- Swelling: When blood pools in the legs, it can create swelling – often uncomfortable.
- Slow healing wounds or ulcers: When oxygen and nutrients can not properly go towards the legs due to poor circulation, it can lead to ulcers or slow healing wounds.
If you notice any of these symptoms, please take time to reach out to a vascular doctor to schedule a consultation immediately. From there, a specialist can evaluate your symptoms, determine a diagnosis, and assist you with any next steps to treat your symptoms.
Poor circulation can be caused by multiple different vascular and health conditions, such as Peripheral Artery Disease, atherosclerosis, and more. Although poor circulation prevention can alleviate symptoms, some diagnoses may require other treatments in addition to preventative measures.
What is Peripheral Artery Disease, and What Does it Have to Do with Poor Circulation?
Peripheral Artery Disease, commonly abbreviated as PAD, occurs when your veins have plaque buildup that makes it harder for your blood to flow through your veins and circulate your blood. Plaque buildup occurs due to high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, and smoking.
PAD develops gradually, but it can be prevented through regular exercise, healthy diet choices, medications, and reducing harmful habits like smoking. By taking preventative measures, you can lower your risk of developing poor circulation in your legs.
What Else Causes Poor Circulation?

PAD is the most common source of poor circulation, but it is not the only diagnosis to go along with poor circulation. Watch out for other conditions that can cause poor circulation, such as:
- Diabetes
- Varicose veins
- Blood clots
- Venous insufficiency
- Raynaud’s disease
- Atherosclerosis
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
A serious condition to highlight in this list is deep vein thrombosis (DVT). With DVT, your circulation is decreased due to a blood clot that has formed in the deep veins in your legs. If this blood clot goes untreated, it can cause a life-threatening pulmonary embolism, where a piece of the clot in your leg breaks off and moves to block blood flow to your lungs.
Keep an eye out for sudden symptoms of swelling, tenderness, or pain in your legs as a sign of DVT. If you experience chest pain, sweating, difficulty breathing, or pale or bluish skin, you could be experiencing a pulmonary embolism, and you should immediately seek medical care.
When Should You Seek Emergency Care?
It’s important to know when symptoms require urgent attention. You should seek emergency care right away if:
- You lose feeling in your foot.
- You notice a persistent “pins and needles” sensation or unexplained pain in your leg—even when you’re resting.
- You have chest pain.
- You suspect you may be experiencing a pulmonary embolism.
Prompt medical attention in these situations can be life-saving and help prevent serious complications.
What Other Factors Can Worsen Circulation Issues?
Blood circulation problems in the legs and feet can be exacerbated by a mix of environmental and genetic factors.
Environmental Influences
- Cold Weather: Exposure to cold environments causes blood vessels to constrict. This constriction slows blood flow, making circulation issues more pronounced.
- Lifestyle Factors: A sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise can heighten circulation problems. Regular movement encourages blood flow, combating the negative effects of cold temperatures.
Genetic Predispositions
- Hereditary Conditions: Some individuals inherit a predisposition to circulatory problems. Conditions like varicose veins can be passed down through family lines.
- Genetic Variants: Specific genetic makeups may influence the efficiency of blood vessels and their ability to transport blood efficiently.
By recognizing these factors, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize aggravating effects, such as dressing warmly in cold weather and maintaining an active lifestyle.
How is Poor Circulation Diagnosed?
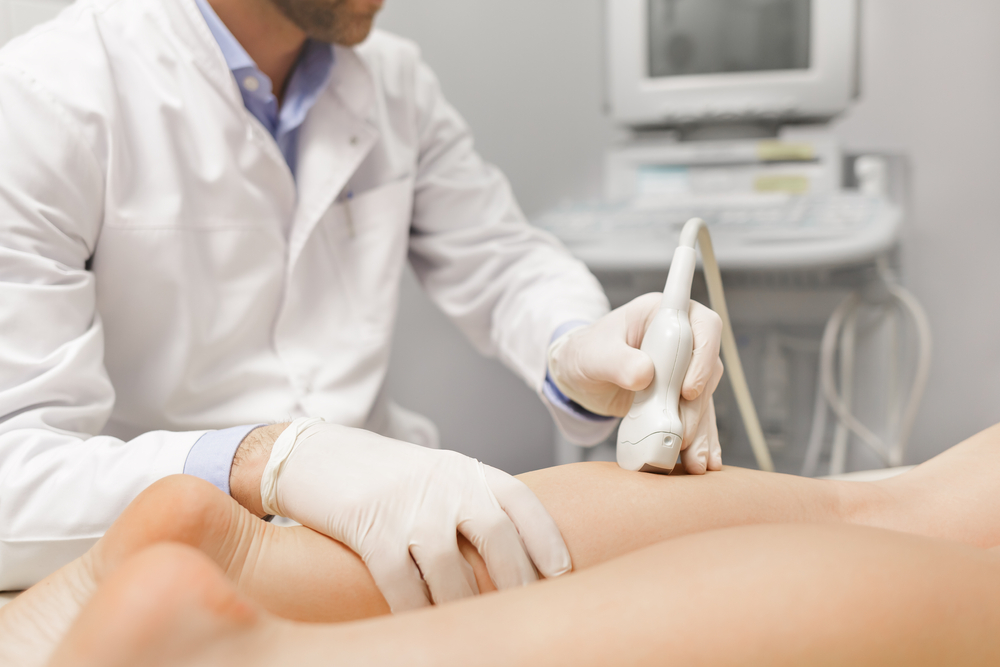
To diagnose the cause of your poor circulation, you should talk to your doctor. After a physical exam, evaluating your medical history, and running some tests, your doctor can determine if you are experiencing poor circulation. Poor circulation is not a diagnosis on its own, but it can point to a more serious condition.
To determine the cause of your poor circulation, your doctor could order a variety of tests, such as:
- Blood tests
- Stress tests: uses exercise to see how your heart responds when it is working its hardest
- Doppler ultrasound
- Angiography: a combination of imaging and contrast material to see where your blood is flowing and locate blockages
- CT scan
- Ankle-brachial index (ABI) test: takes the blood pressure in your arm and compares it to the blood pressure in your ankle
- Segmental Doppler pressure testing
Questions to Discuss With Your Doctor
If you suspect poor circulation or have received a related diagnosis, it’s important to have a thorough conversation with your healthcare provider. Consider bringing these questions to your next appointment:
- What lifestyle changes or exercises are best for improving my circulation, considering my current health status?
- Are there medications or therapies that I should consider, or would lifestyle changes be sufficient at this stage?
- Are there any activities—or over-the-counter remedies—I should avoid?
- Are additional tests necessary to pinpoint the cause of my symptoms?
- How can I best monitor my symptoms at home, and what warning signs should prompt a return to the office or a call for urgent care?
- Should I be concerned about potential complications, such as blood clots?
- Would it be helpful to see a specialist, like a vascular surgeon or a cardiologist?
Asking clear, specific questions can help you and your doctor create an effective plan to manage and improve your circulation.
How to Improve Leg Circulation
There are practical ways to improve leg circulation and ensure that the blood continues flowing!
Here are some ways you can improve leg circulation daily:
- Daily exercise: Aim for daily low-impact exercises to keep the blood flowing with activities like walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Daily stretching: Stretching daily can also promote leg circulation with stretches like ankle pumps and leg lifts.
- Daily leg elevation: Elevating legs daily helps blood to return back to the heart and decreases swelling.
- Daily hydration: Hydration is key to ensure blood is circulating properly in the legs, as blood needs water to keep flowing.
Treatment Options for Poor Leg Circulation
When seeking treatment for poor circulation, it is important to know which condition your circulation issues stem from to determine the best course of action. With PAD, there are non-surgical procedures that can improve circulation, but you may need a different treatment for other conditions.
Common PAD procedures include:
- Angioplasty: A catheter guides a small balloon into your artery so it can be inflated to compress the blockage
- Atherectomy: A laser or rotating catheter scrapes the plaque buildup way from your artery walls
- Stent placement: A mesh stent is inserted into your artery to keep it permanently open while preventing the plaque buildup from breaking off
There are some generalized treatments for poor circulation that you can expect regardless of the condition causing it. Each treatment aims to open up your arteries or to reduce blockages such as plaque and blood clots.
Angioplasties can be used for more than just PAD, as they work to open arteries by compressing blockages. Removing blood clots and varicose veins can also open arteries and improve circulation.
A variety of medications can be used to reduce your chances of blockages. Blood thinners and anti-platelet medications can be used to reduce your risk of blood clots. Statins are prescription medications that reduce how much plaque builds up in your arteries.These medications do create a risk of bleeding, but with the proper dosage you shouldn’t experience any issues.
Potential Complications and Side Effects
It’s important to note that, like any surgical procedure, treatments aimed at improving circulation—including angioplasty and procedures to remove blockages—carry a risk of bleeding. This is also true for medications that reduce clotting. Your healthcare provider will carefully monitor and adjust your dosage so that you receive the benefits of these medications without excessive risk of bleeding when you get hurt or injured. Open communication with your provider about any unusual bruising or bleeding is key to staying safe while on these therapies.
What Happens if Poor Circulation Goes Untreated?
Without treatment, poor circulation only continues to get worse. Blood circulation plays a vital role in your body’s healing process, which means small injuries will require much more time to heal. This can lead small injuries to become infected or get worse over time as well.
If you don’t address poor circulation, it’s unlikely to improve on its own—and often, it can actually progress. Worsening symptoms may include increased pain, swelling, numbness, or color changes in your extremities. Without intervention, you may find yourself at higher risk for complications such as chronic wounds, ulcers, skin infections, or even more serious issues like tissue damage.
Fortunately, you aren’t powerless against poor circulation. There are effective ways to manage and improve your symptoms through lifestyle changes, medications, and, in some cases, surgical procedures. Early intervention can help restore healthy blood flow, reduce discomfort, and prevent complications down the road.
What Can I Do to Prevent Poor Foot Circulation?
There are several preventative measures you can take in addition to treatments and medications. Evaluating your current lifestyle and making changes can have a significant impact on your symptoms. Here are some suggestions to get you started:
- Quit smoking
- Limit how much alcohol you drink
- Stay hydrated
- Reduce your caffeine intake
- Exercise regularly
- Remember to stretch
- Elevate your legs
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Manage a healthy weight
Although these changes can alleviate your symptoms, they are not going to cure your symptoms. Conditions causing poor circulation cannot not be completely cured, only managed.
Living with Poor Circulation
Once you have a diagnosed condition and a treatment plan, you can enjoy life while taking care of your cardiovascular health. Make sure you still have regular doctor appointments, take any medications you are prescribed, make healthy lifestyle changes, and watch out for other symptoms.
Treatment at Michigan Vascular
At Michigan Vascular Center, we’re committed to providing the highest quality care and support for our patients based on sound principles of vascular disease treatment. If you believe you have poor circulation, let us help determine the cause and develop a treatment plan for you.
Contact us today to learn more about our services and how we can help you manage your poor circulation.
FAQs about Poor Circulation
Needing treatment and relief from poor circulation? Contact us above and we’d be happy to schedule an appointment for you to connect with one of our providers. Our goal at Michigan Vascular is to treat each patient with quality care and treatment for all major vascular disorders. With over 50 years in the world of vascular health, our team is skilled and equipped to handle a variety of vascular conditions.

