As you get older, regular health screenings become more important than ever before, especially for men over 50 years old. There are many health conditions that you have an increased risk of developing, including heart disease, certain cancers, diabetes, and more. Thankfully, you can take preventative measures and use 10 different health tests to ensure you don’t miss any health conditions.
1. Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI)
During an ankle brachial index test, a doctor compares your blood pressure in your ankle to your blood pressure in your arm. This test is used to determine if you have peripheral artery disease, which is a condition where the arteries in your legs become narrow or blocked and the blood flow in your legs is reduced.
Peripheral artery disease can increase your risk of a heart attack or stroke, but with early intervention it can be managed. Men over 50 with a history of heart disease, diabetes, or smoking are predisposed to developing PAD, but there is no harm in getting this test done as a preventative measure.
2. Cholesterol and Blood Pressure Check
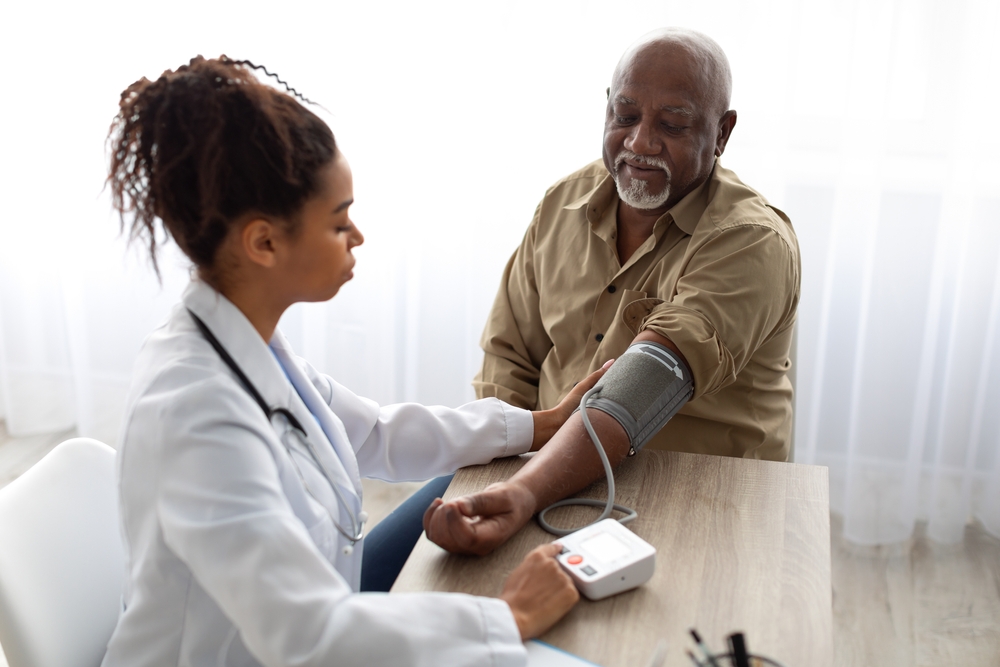
Regularly having your cholesterol levels and blood pressure checked is a great way to assess your cardiovascular risks. Without proper treatment, high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels can lead to developing heart disease or cause a stroke.
It’s common for your doctor to check your cholesterol levels about every five years. However, you could have more frequent checks if you have risk factors such as diabetes, obesity, or smoking. Cholesterol tests require your blood to be drawn and sent to a lab where they will measure your LDL and HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and overall cholesterol levels. Without intervention, high cholesterol can lead to a stroke, peripheral artery disease, or renal artery disease.
Blood pressure checks are much more common, as doctors measure your blood pressure regularly to develop a baseline for your medical history. Once you begin to present with elevated blood pressure, your doctors can start to take steps to intervene. You should have your blood pressure checked at least once a year.
3. Colon Cancer Screening
One of the most common cancers for men as they get older is colorectal cancer. Thankfully, colorectal cancer can be caught early with routine screenings. You should expect your doctor to start screenings around 45 years old, but this timeline could be moved up if you have a family history of colorectal cancer or additional risk factors.
Colorectal cancer screenings can involve different tests, with the most common being colonoscopies and stool tests. It is recommended for men over the age of 45 to get colonoscopies every 10 years if they don’t have an increased risk of colorectal cancer.
During a colonoscopy, a doctor uses a camera to inspect your colon and remove any precancerous polyps they find. Stool tests can be done more regularly to detect abnormal DNA or blood, which can point towards colorectal cancer.
4. Diabetes Screening
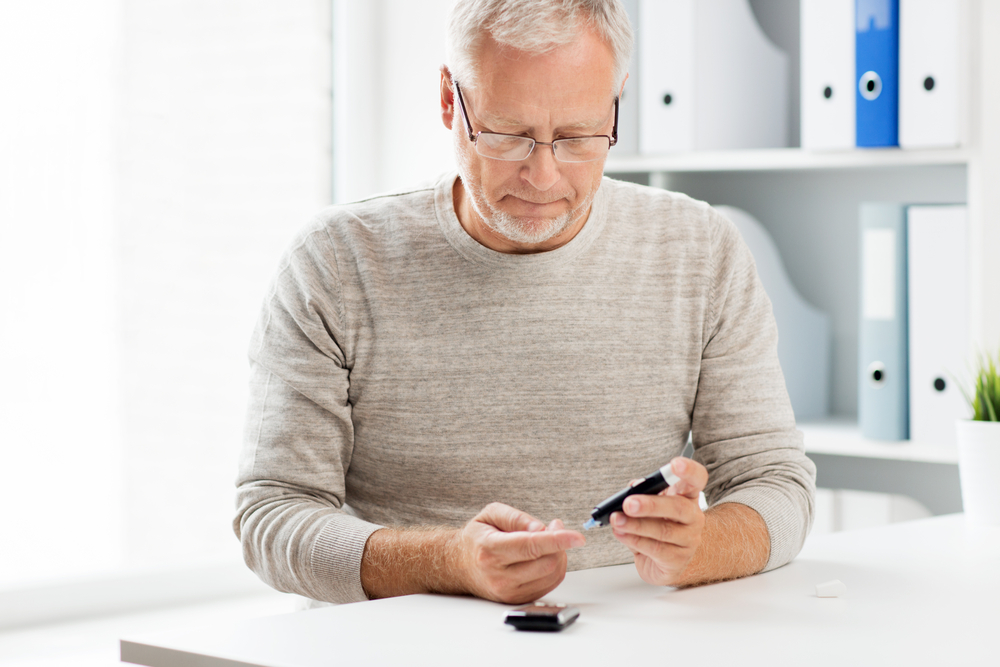

For men around 50, diabetes screening can be incredibly important as diabetes increases your risk of kidney failure, heart disease, and other health issues. If you are overweight or have a family history of diabetes, you will need to be screened annually or biannually.
All diabetes tests involve measuring the glucose levels in your blood, commonly referred to as blood sugar levels. Your doctor will assess your blood sugar levels over 2-3 months to determine your average blood sugar level. You can also expect to have your blood tested after an overnight fast and before and after eating sugar to assess how your body reacts.
When diabetes is left untreated, it can lead to peripheral artery disease and venous disease, both of which can affect your quality of life.
5. Prostate Cancer Screening
Another common cancer for men is prostate cancer. Prostate cancer is usually a slow-growing cancer and can be treatable if it is caught early. Men over 50 should get a prostate exam every 2-4 years. If you have a family history of prostate cancer, you should consider having a prostate exam around 40-45 years old.
Screening for prostate cancer involves a digital rectal exam and a prostate-specific antigen blood test. Digital rectal exams require a doctor to insert a gloved finger into the rectum to check the prostate for any abnormalities. PSA blood tests look for elevated PSA levels, as prostate cancer can cause more PSA protein to be produced.
6. Vitamin D Test
As you get older, something as simple as a vitamin deficiency can affect your health. Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to depression, muscle weakness, osteoporosis, and immune system issues. If you are over 50 and experiencing muscle pain, fatigue, or bone weakness, you should talk to your doctor about a vitamin D test. After a blood test, your doctor can give advice on supplements, diet changes, and sun exposure to help manage your symptoms.
7. Dermatology Check

Over time, your skin is exposed to a number of factors that can increase your risk of developing skin cancer. Skin cancers, like melanoma, can become life-threatening if left untreated. When skin cancer is caught early, it can be treatable. Make sure to check your skin regularly for new growths or changes to any moles. Visiting a dermatologist annually can ensure you don’t miss any suspicious growths, abnormal moles, or lesions.
8. Testicular Cancer Screening
Although screening for testicular cancer starts when you are young, it’s important to continue getting screenings as you get older. Testicular cancer screenings are a common part of a routine checkup with your doctor, where they will examine your testicles for any abnormal lumps or swelling. If needed, your doctor may send you for an ultrasound to assess if you need further testing.
You should self-examine your testicles monthly to look for lumps or swelling, which could indicate testicular cancer. If you notice any changes in your testicles during a self exam, see your doctor as soon as possible for further examination.
9. Glaucoma Screening
Your eyes are not immune to the effects of aging. Over time, fluid can build up in your eye and cause you to develop glaucoma. Glaucoma is a chronic condition that damages your optic nerve, and without treatment it can lead to vision loss and blindness. Glaucoma can begin to form at any age, but it is more common in adults 40 years or older.
For men over 50, it is recommended to get regular eye exams every 1-2 years. During an eye exam, your doctor will perform a tonometry test to measure your eye pressure, an ophthalmoscopy to allow your doctor to examine your optic nerve, and a visual field test to assess your peripheral vision. If you have diabetes or a family history of diabetes, you are at a higher risk of developing glaucoma.
10. Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Screening
An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a bulge in your aorta, the largest artery in your body. AAAs occur when your aorta wall is weakened, allowing it to become enlarged. As AAAs progress, they can rupture and cause fatal internal bleeding.
Although most men don’t get screened for AAA until they are 65, if you have a history of high blood pressure, heart disease, smoking, or a larger aorta, you should talk to your doctor about getting a screening. AAAs can be diagnosed through an ultrasound and assessed to determine if surgery is needed.
Treatment with Michigan Vascular
At Michigan Vascular Center, we’re committed to providing the highest quality care and support for our patients based on sound principles of vascular disease treatment. If you believe you are at risk of vascular disease, let us help determine the cause and develop a treatment plan for you.
Contact us today to learn more about our services and how we can help you stay on top of your long-term health with regular testing and screening services

